Introduction
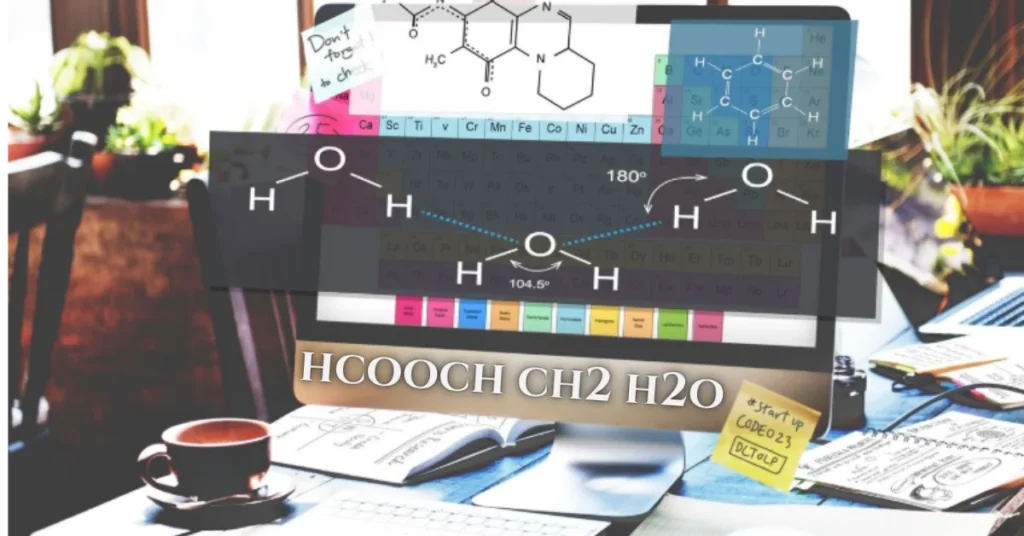
The world of industrial chemistry often revolves around simple reactions with massive implications. One such transformation involves the compound HCOOCH CH2 and H2O—a hydrolysis process that is not only scientifically fascinating but also immensely valuable in manufacturing, green chemistry, and pharmaceuticals. In this article, we’ll dive into the mechanism behind this reaction and explore its broad impact on industry and innovation.
Understanding the Chemical Formula
What Does HCOOCH CH2 Represent?
While the shorthand “HCOOCH CH2” looks intimidating, it’s a simplified notation often used for vinyl formate (HCOOCH=CH2). This compound contains both a formate ester and a vinyl group, making it highly reactive and useful for chemical transformations.
The Role of Water in the Reaction
Water (H2O) serves as a reactant in the hydrolysis reaction, breaking the ester bond in vinyl formate. This reaction leads to the formation of formic acid and vinyl alcohol, although vinyl alcohol quickly rearranges to acetaldehyde.
Functional Groups Involved
- Ester group: The site where water attacks during hydrolysis.
- Vinyl group: Adds reactivity and potential polymerization interest.
- Formyl group: Converts into formic acid post-reaction.
Hydrolysis Reaction Explained
Mechanism of Hydrolysis
The hydrolysis of vinyl formate involves a nucleophilic attack by water on the carbonyl carbon of the ester group, forming an unstable intermediate which then collapses to release formic acid and vinyl alcohol.
General reaction:
HCOOCH=CH2 + H2O → HCOOH + CH2=CHOH → CH3CHO (acetaldehyde)
Catalysts and Conditions
- Acidic or basic conditions can accelerate the reaction.
- Mild temperatures are often sufficient, though industrial setups optimize for reaction speed and yield.
Products Formed from the Reaction
- Formic Acid (HCOOH) – Widely used in leather processing, agriculture, and cleaning products.
- Acetaldehyde (via tautomerism) – A key intermediate in perfumery, flavors, and other chemical syntheses.
Industrial Applications
Use in Polymer and Resin Production
Vinyl formate is a precursor for producing vinyl polymers and copolymers. Its breakdown allows manufacturers to tailor polymer properties more precisely.
Role in Pharmaceuticals
Hydrolysis products like formic acid are used in pharmaceutical intermediates, contributing to drug formulation and synthesis.
Application in Green Chemistry
Because vinyl formate hydrolysis is atom-efficient and produces minimal hazardous waste, it’s aligned with green chemistry principles.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Waste Management and Byproducts
While generally clean, care must be taken with:
- Acetaldehyde, which is volatile and potentially harmful.
- Formic acid, which is corrosive in concentrated form.
Safety in Handling Reactants
- Use gloves and eye protection.
- Work in ventilated areas or fume hoods due to volatile product formation.
Eco-Friendly Reaction Engineering
By adjusting pH and minimizing solvents, this reaction can be engineered to be low-waste and energy-efficient, especially in closed-loop systems.
Experimental Techniques
Lab Setup for Hydrolysis
Typical setup includes:
- Reflux apparatus
- pH meter
- Magnetic stirrer
Monitoring pH and Temperature
Hydrolysis often proceeds better under slightly acidic or basic conditions. Monitoring ensures maximum conversion without side reactions.
Identifying Products (GC, IR, NMR)
- Gas Chromatography (GC): Detects volatile products like acetaldehyde.
- Infrared Spectroscopy (IR): Confirms the presence of –OH and C=O groups.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): Gives detailed insight into molecular structure post-reaction.
Challenges in Reaction Scaling
Lab-Scale vs Industrial-Scale Hydrolysis
What works in a test tube may not scale easily. Industrial setups require:
- Flow reactors
- Efficient heat exchangers
- Product separation units
Purity and Yield Optimization
Purification steps like distillation or crystallization help maintain high product quality, especially for food-grade or pharmaceutical uses.
Cost and Energy Efficiency
The reaction is relatively low-energy, but cost of vinyl formate synthesis and equipment corrosion can be challenges.
Real-World Case Studies
Industry Use Examples
- BASF and other chemical giants use vinyl formate hydrolysis in polymer feedstock production.
- EcoChem Ltd. uses the process in bio-solvent formulations.
Innovations Using HCOOCH CH2
Recent startups are exploring bio-derived vinyl formate, making the hydrolysis reaction even greener.
Circular Chemistry Concepts
Hydrolysis products can be fed into biodegradable product cycles, making the chemistry loop sustainable and regenerative.
Conclusion
The reaction involving HCOOCH CH2 and H2O is more than a classroom exercise—it’s a pillar of modern industrial chemistry. With its clean conversion, valuable products, and scalable potential, this hydrolysis reaction is shaping how industries approach both efficiency and sustainability. Whether you’re a student, a chemist, or just chemistry-curious, this simple formula packs a powerful impact.
ALSO READ: gomyfinance.com Credit Score Guide to Boost Financially
FAQs
What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O used for?
This reaction forms the basis for producing formic acid and acetaldehyde, useful in polymers, pharmaceuticals, and green solvents.
What products result from its hydrolysis?
Formic acid and vinyl alcohol (which rearranges into acetaldehyde) are the main products.
Is this reaction eco-friendly?
Yes, it’s atom-efficient, low-waste, and aligns with green chemistry standards when properly managed.
What industries benefit from this process?
Chemical manufacturing, pharma, polymer production, and sustainable materials industries benefit greatly.
Can the reaction be done in a basic home lab?
Technically yes, but due to safety concerns with volatile products, it’s best done in a controlled lab environment.